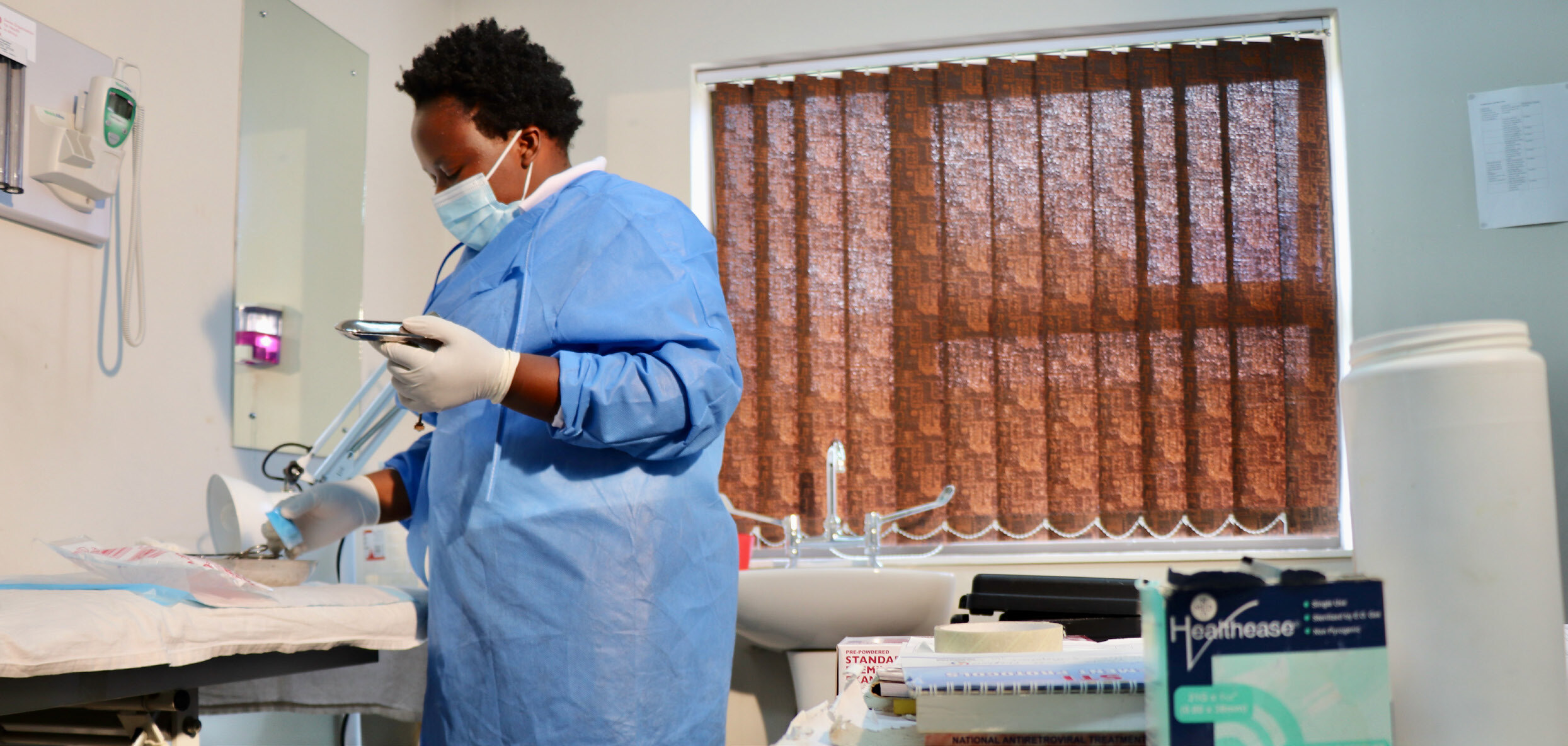
Women living with HIV are at a 5 times increased risk of getting infected with HPV, which can lead to pre-cancerous lesions (cell growths) that grow. If left untreated, uncontrolled cell growth can turn into cancer. Being infected with HPV can also increase the risk of being infected with HIV for both men and women. Women living with HIV are more likely to get cervical cancer at a younger age, often around the age of 35 years and beyond, especially if not on antiretroviral therapy (ART). If a woman living with HIV develops cervical cancer, symptoms could progress and worsen more rapidly.
Because of the risks associated between HIV and HPV it is important for young people both young men and young women to understand steps to prevent HPV infection (vaccines!) and ways to catch it early (screening!).