The burden of tuberculosis (TB) in children and adolescents remains very significant. Several million children and adolescents are infected with TB each year worldwide following exposure to an infectious TB case and the risk of progression from TB infection to tuberculosis disease is higher in this group compared to adults. This review describes the risk factors for TB infection in children and adolescents. Following TB exposure, the risk of TB infection is determined by a combination of index case characteristics, contact features, and environmental determinants. We also present the recently recommended approaches to diagnose and treat TB infection as well as novel tests for infection. The tests for TB infection have limitations and diagnosis still relies on an indirect immunological assessment of cellular immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using immunodiagnostic testing. It is recommended that TB exposed children and adolescents and those living with HIV receive TB preventive treatment (TPT) to reduce the risk of progression to TB disease. Several TPT regimens of similar effectiveness and safety are now available and recommended by the World Health Organisation.
Explore Related Resources
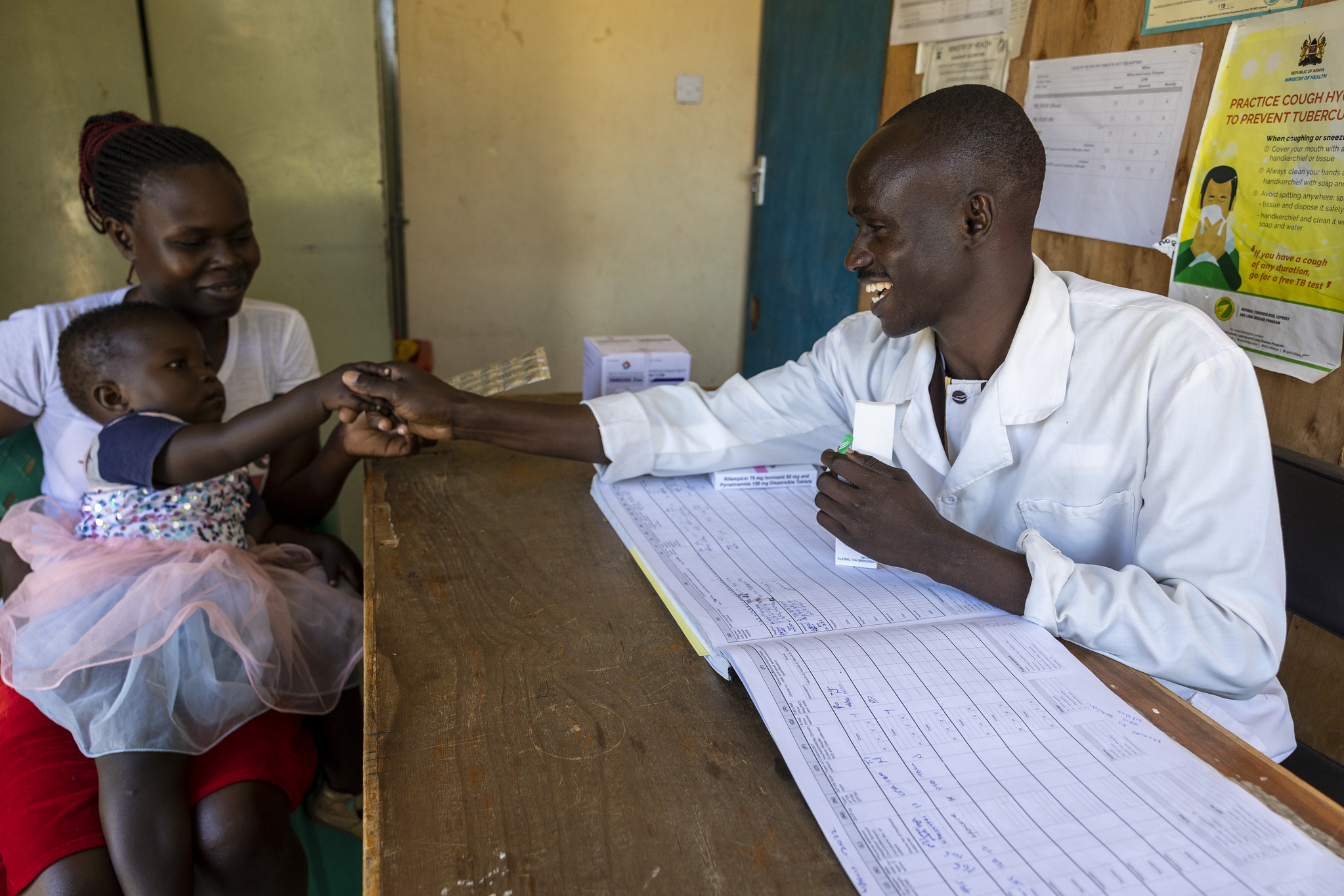
Child,Precious Ogweno accompanied by caregiver Leah Ogweno, at the TB clinic -HEI in Mbita sub county hospital, Mbita, Homabay. Photo by Kevin Ouma for EGPAF.
Journal Articles
Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment Uptake Among Patients Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy in Malawi: Children Left Behind
Published November 2025
Background: Tuberculosis preventive treatment (TPT) is recommended for people living with HIV (PLHIV) to reduce the tuberculosis (TB) incidence in regions with a high prevalence of TB. We evaluated the uptake and completion of TPT among newly initiated antiretroviral therapy (ART) patients in a programme setting in Malawi. Objectives: To describe TPT initiation and completion rates, and […]
View Resource
Topics:
Pediatric Tuberculosis (TB),
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Malawi

Journal Articles
Effect of integrating paediatric tuberculosis services into child healthcare services on case detection in Africa
Published December 2024
Introduction Paediatric tuberculosis (TB) underdiagnosis is a critical concern. The INPUT stepped-wedge cluster-randomised trial assessed the impact of integrating child TB services into child healthcare on TB case detection among children under age 5 years. Methods We compared the standard of care, providing TB care in specific TB clinics (control phase), with the Catalysing Paediatric […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Cameroon,
Kenya

Journal Articles
Decentralisation and integration of paediatric tuberculosis services to primary healthcare facilities as an approach to optimise management in Cameroon and Kenya
Published October 2024
Introduction: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality for children less than 5 years. Diagnosis and treatment of children with active TB is often centralised in district hospital settings due to poor public health infrastructure and lack of diagnostic capabilities in primary healthcare (PHC) facilities. This analysis aims to evaluate TB case detection […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Cameroon,
Kenya

