Individual leadership and leaders have played pivotal roles in the history of efforts to end the AIDS epidemic. The goal of this article is to reflect on and understand how leadership and leaders have impacted and enabled the success of the Global Plan Towards the Elimination of New HIV Infections among Children by 2015 and Keeping their Mothers Alive (Global Plan). To accomplish this goal, multiple interviews were conducted with individuals in positions of leadership who had been identified as people whose actions drove progress. Interviewees were selected from all levels of traditional hierarchies and sectors to provide a more complete account and representation of leadership, with a particular emphasis on the community, district, and country levels. The leaders interviewed provide insight into their work, motivations, and approaches to effective leadership. Through their experiences, they shed light on the strategies they used to drive changes in policy, programs, practice, and communities that allowed for progress toward the goals of the Global Plan. Leaders also identify future challenges and areas of improvement in the effort to end the AIDS epidemic that they feel require leadership and urgent action. In conclusion, this article identifies common characteristics of effective leadership and reflects on the experiences of individuals who are leaders in the effort to end the AIDS epidemic, and how their lessons learned can be applied to help realize future global public health goals.
Explore Related Resources
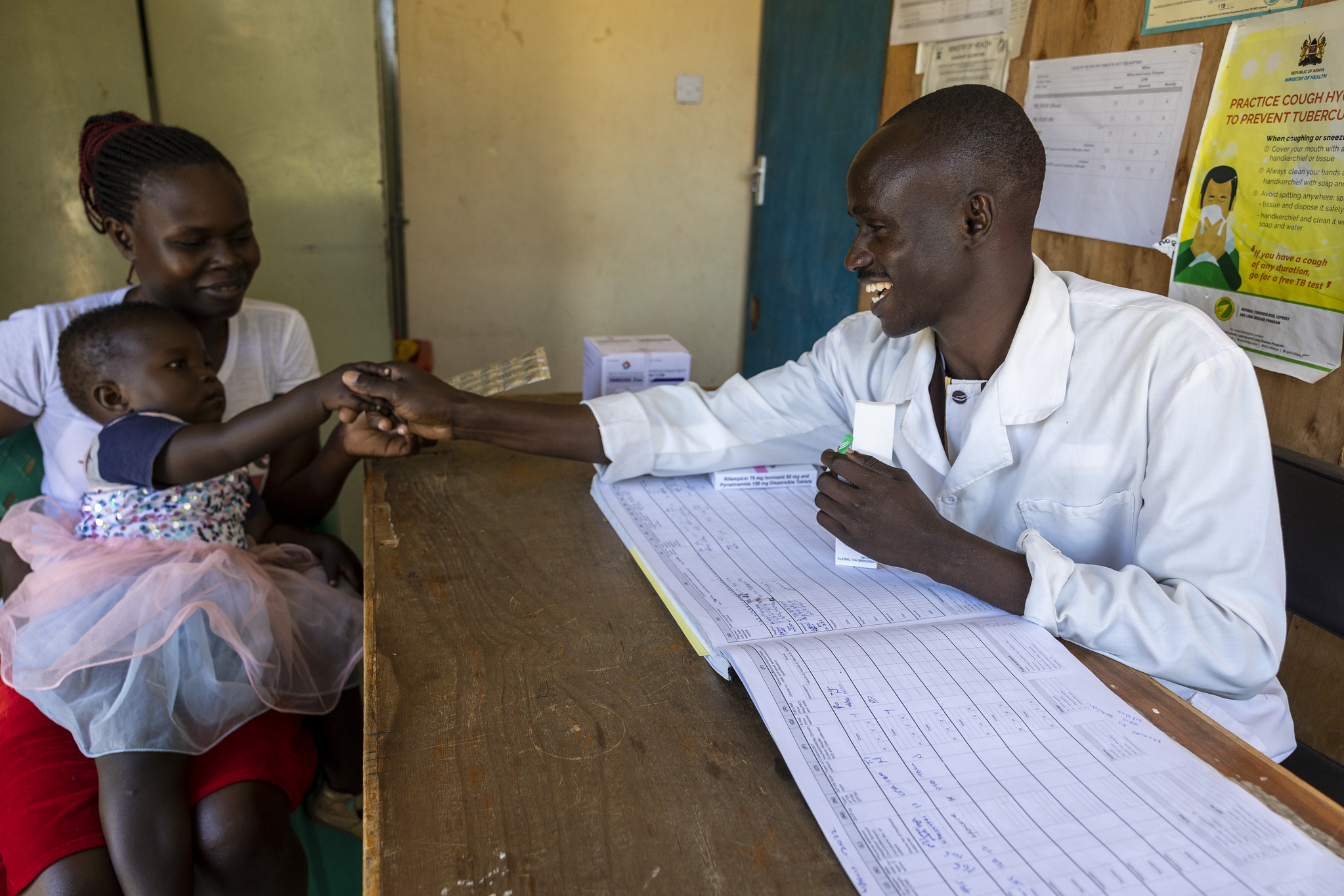
Child,Precious Ogweno accompanied by caregiver Leah Ogweno, at the TB clinic -HEI in Mbita sub county hospital, Mbita, Homabay. Photo by Kevin Ouma for EGPAF.
Journal Articles
Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment Uptake Among Patients Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy in Malawi: Children Left Behind
Published November 2025
Background: Tuberculosis preventive treatment (TPT) is recommended for people living with HIV (PLHIV) to reduce the tuberculosis (TB) incidence in regions with a high prevalence of TB. We evaluated the uptake and completion of TPT among newly initiated antiretroviral therapy (ART) patients in a programme setting in Malawi. Objectives: To describe TPT initiation and completion rates, and […]
View Resource
Topics:
Pediatric Tuberculosis (TB),
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Malawi

Project Brief
Integrating Nurturing Care for Early Childhood Development into Primary Health Care: The Tanzania Experience
Published July 2025
Overview More than 275 million children in low- and middle-income countries are at risk of suboptimal development, including over 66% of children in sub-Saharan Africa. In Tanzania 43% of children are at high risk of not achieving their full potential for growth and development. Risk factors for suboptimal development include poverty, nutritional deficiencies, maternal depression, […]
View Resource
Countries:
Tanzania
Resource
Effectiveness of a Multi-component Facility-based Intervention on HIV-related Infant and Maternal Outcomes
Published April 2025
Introduction Even in the context of widespread access to prevention of vertical HIV transmission (PVT) services, health system challenges compromise health outcomes for women living with HIV and their children. The “Integrated Management Team to Improve Maternal-Child Outcomes” (IMPROVE) study measured the effect of a package of facility-based interventions on PVT and maternal and child […]
View Resource
Countries:
Lesotho

