In this review, we discuss considerations and successful models for providing decentralized diagnosis, treatment, and prevention services for children and adolescents. Key approaches to building decentralized capacity for childhood TB diagnosis in primary care facilities include provider training and increased access to child-focused diagnostic tools and techniques. Treatment of TB disease should be managed close to where patients live; pediatric formulations of both first- and second-line drugs should be widely available; and any hospitalization should be for as brief a period as medically indicated. TB preventive treatment for child and adolescent contacts must be greatly expanded, which will require home visits to identify contacts, building capacity to rule out TB, and adoption of shorter preventive regimens. Decentralization of TB services should involve the private sector, with collaborations outside the TB program in order to reach children and adolescents where they first enter the health care system. The impact of decentralization will be maximized if programs are family-centered and designed around responding to the needs of children and adolescents affected by TB, as well as their families. View Full-Text
Explore Related Resources
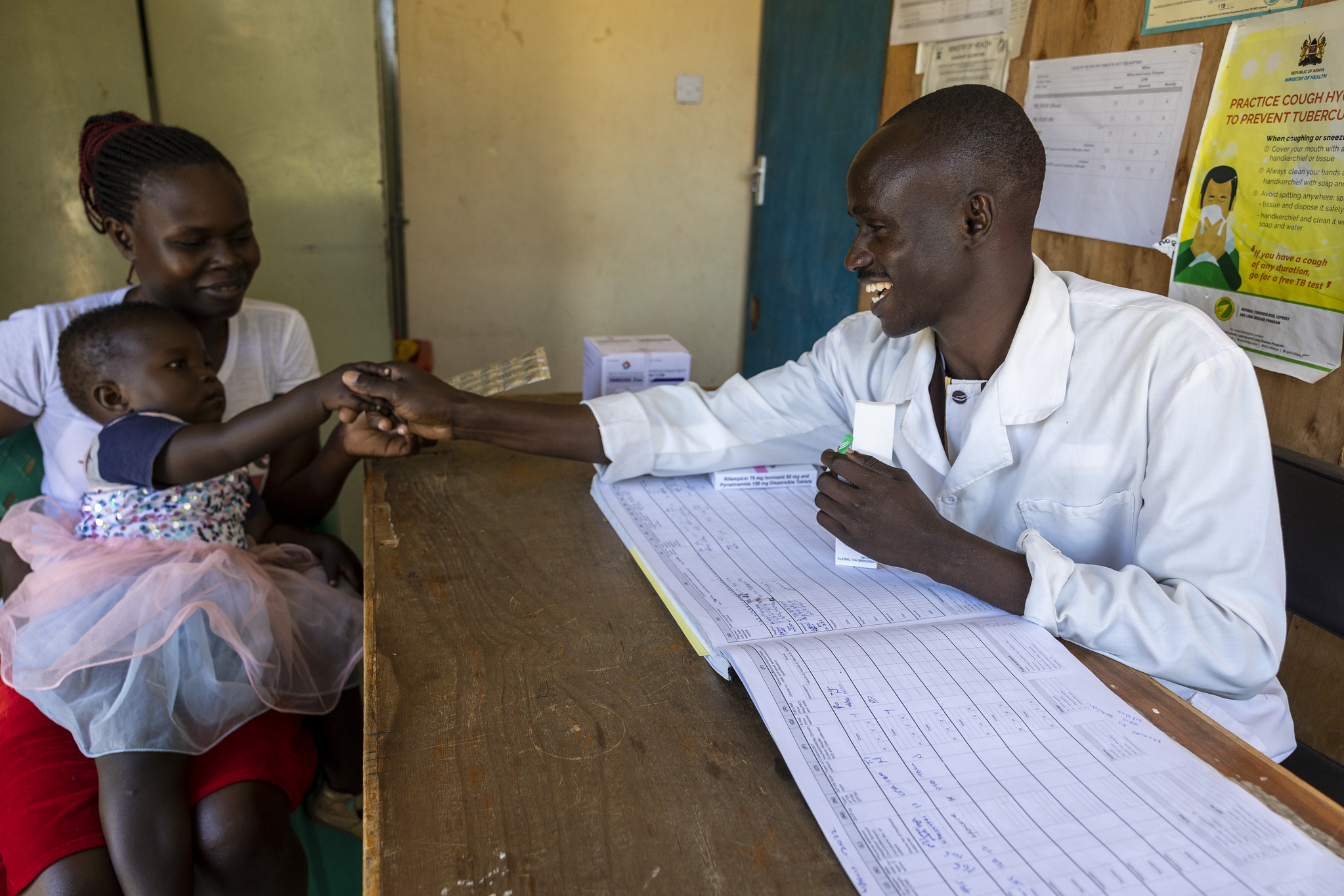
Child,Precious Ogweno accompanied by caregiver Leah Ogweno, at the TB clinic -HEI in Mbita sub county hospital, Mbita, Homabay. Photo by Kevin Ouma for EGPAF.
Journal Articles
Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment Uptake Among Patients Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy in Malawi: Children Left Behind
Published November 2025
Background: Tuberculosis preventive treatment (TPT) is recommended for people living with HIV (PLHIV) to reduce the tuberculosis (TB) incidence in regions with a high prevalence of TB. We evaluated the uptake and completion of TPT among newly initiated antiretroviral therapy (ART) patients in a programme setting in Malawi. Objectives: To describe TPT initiation and completion rates, and […]
View Resource
Topics:
Pediatric Tuberculosis (TB),
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Malawi

Journal Articles
Effect of integrating paediatric tuberculosis services into child healthcare services on case detection in Africa
Published December 2024
Introduction Paediatric tuberculosis (TB) underdiagnosis is a critical concern. The INPUT stepped-wedge cluster-randomised trial assessed the impact of integrating child TB services into child healthcare on TB case detection among children under age 5 years. Methods We compared the standard of care, providing TB care in specific TB clinics (control phase), with the Catalysing Paediatric […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Cameroon,
Kenya
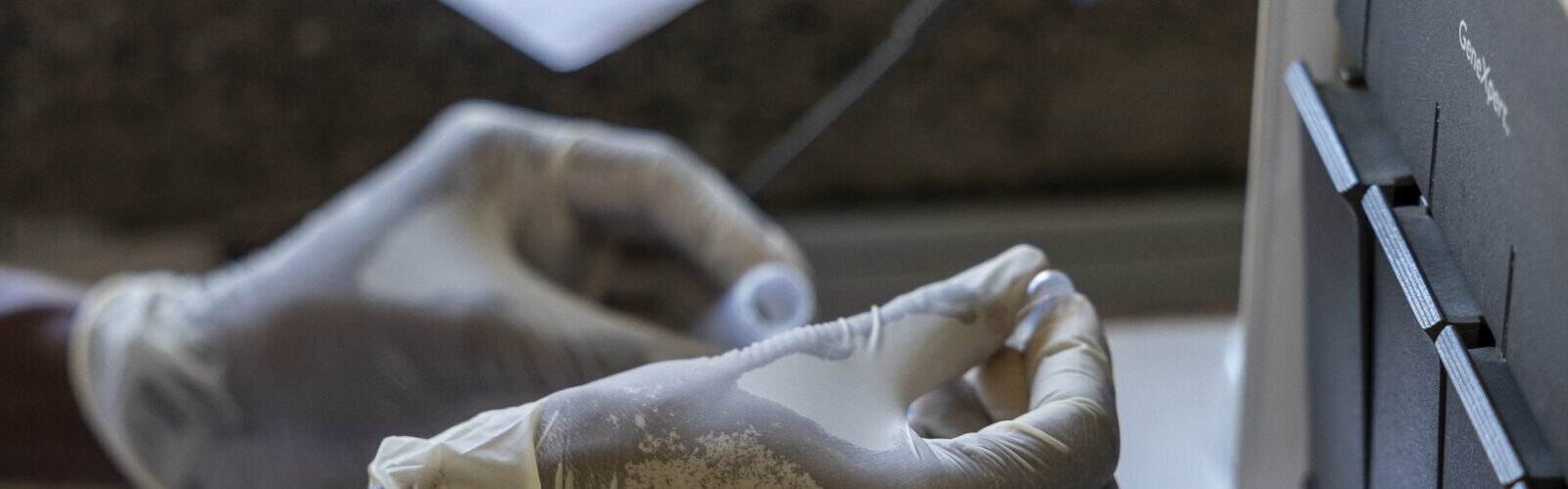

Laboratory technician testing blood samples from facilities in Mbita sub county hospital, Mbita,Homabay. Photo by Kevin Ouma for EGPAF
Journal Articles
Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents
Published November 2024
The burden of tuberculosis (TB) in children and adolescents remains very significant. Several million children and adolescents are infected with TB each year worldwide following exposure to an infectious TB case and the risk of progression from TB infection to tuberculosis disease is higher in this group compared to adults. This review describes the risk […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)

