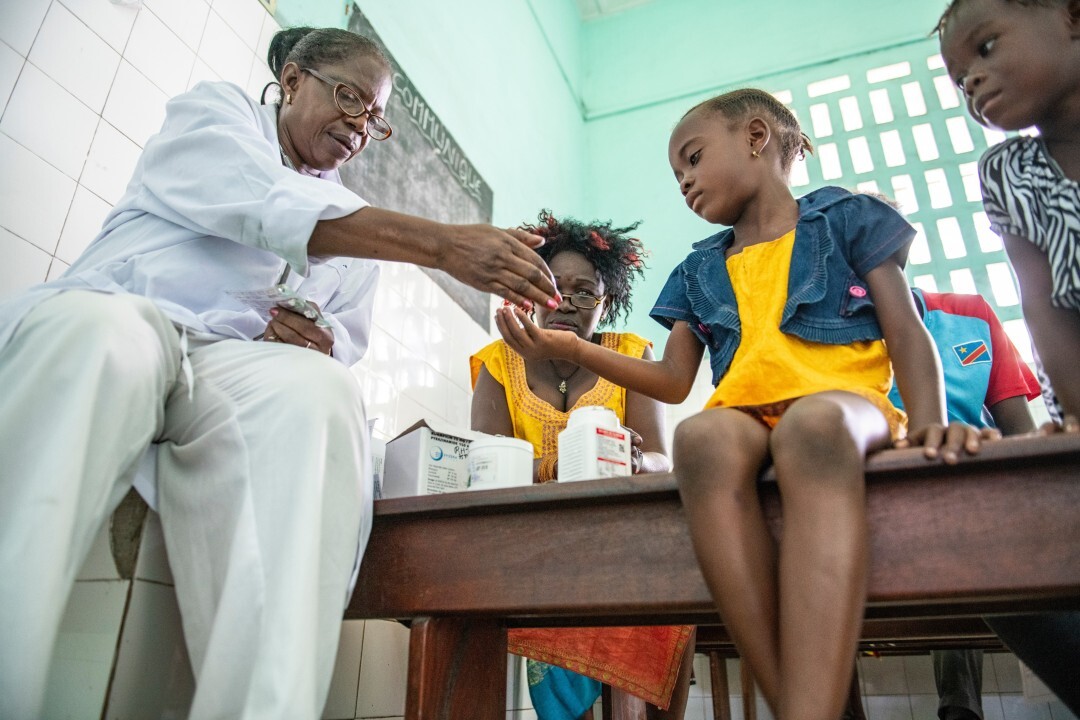Tuberculosis is among the top-10 causes of mortality in children with more than 1 million children suffering from TB disease annually worldwide. The main challenge in young children is the difficulty in establishing an accurate diagnosis of active TB. The INPUT study is a stepped-wedge cluster-randomized intervention study aiming to assess the effectiveness of integrating TB services into child healthcare services on TB diagnosis capacities in children under 5 years of age. Study enrolments started in May 2019, enrolments will be completed in October 2020 and follow-up will be completed by June 2021. The study findings will be disseminated to national, regional and international audiences and will inform innovative approaches to integration of TB screening, diagnosis, and treatment initiation into child health care services.
Explore Related Resources

Journal Articles
Effect of integrating paediatric tuberculosis services into child healthcare services on case detection in Africa
Published December 2024
Introduction Paediatric tuberculosis (TB) underdiagnosis is a critical concern. The INPUT stepped-wedge cluster-randomised trial assessed the impact of integrating child TB services into child healthcare on TB case detection among children under age 5 years. Methods We compared the standard of care, providing TB care in specific TB clinics (control phase), with the Catalysing Paediatric […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Cameroon,
Kenya
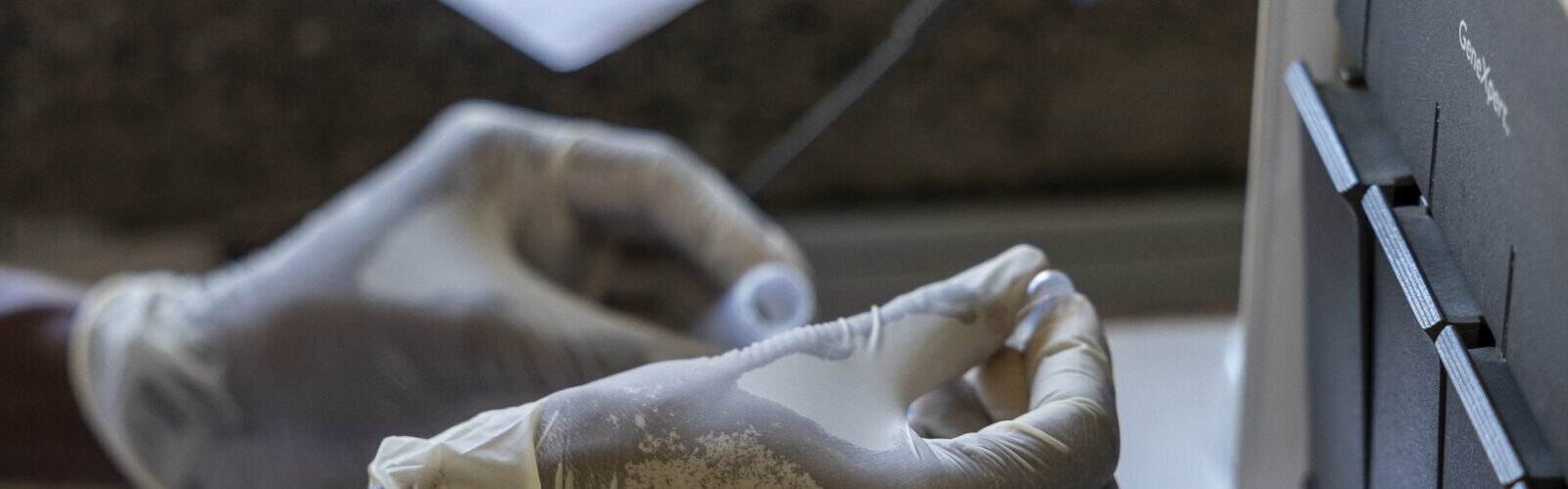

Laboratory technician testing blood samples from facilities in Mbita sub county hospital, Mbita,Homabay. Photo by Kevin Ouma for EGPAF
Journal Articles
Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents
Published November 2024
The burden of tuberculosis (TB) in children and adolescents remains very significant. Several million children and adolescents are infected with TB each year worldwide following exposure to an infectious TB case and the risk of progression from TB infection to tuberculosis disease is higher in this group compared to adults. This review describes the risk […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)

Journal Articles
Decentralisation and integration of paediatric tuberculosis services to primary healthcare facilities as an approach to optimise management in Cameroon and Kenya
Published October 2024
Introduction: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality for children less than 5 years. Diagnosis and treatment of children with active TB is often centralised in district hospital settings due to poor public health infrastructure and lack of diagnostic capabilities in primary healthcare (PHC) facilities. This analysis aims to evaluate TB case detection […]
View Resource
Topics:
Tuberculosis (TB)
Countries:
Cameroon,
Kenya